The rise in manufacturing carbon emissions has become a pressing concern in the face of global climate change. As industries ramp up production to meet growing consumer demand, the reliance on fossil fuels and energy-intensive processes often leads to increased greenhouse gas emissions. This trend poses significant challenges, not only to the environment but also to sustainability efforts across various sectors. Understanding the factors contributing to the escalation of manufacturing carbon emissions is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
Industrial activities account for a substantial portion of global carbon emissions, and the complexity of manufacturing processes makes it difficult to pinpoint singular causes. Factors such as outdated technologies, inefficiencies in energy use, and a lack of regulatory frameworks often exacerbate the problem. Moreover, the globalization of supply chains has led to increased emissions as manufacturers seek to cut costs and maximize production, sometimes at the expense of environmental considerations. To tackle rising manufacturing carbon emissions, a multifaceted approach involving innovation, regulatory action, and investment in cleaner technologies is essential.
By exploring the underlying causes and potential solutions to manufacturing carbon emissions, stakeholders can work towards a more sustainable future. Implementing energy-efficient practices, adopting renewable energy sources, and fostering collaboration between governments and industries are vital steps in this journey. As global awareness of climate issues grows, it is imperative to prioritize strategies that not only reduce emissions but also promote economic resilience and environmental stewardship.

The manufacturing sector is a significant contributor to global carbon emissions, with several factors driving this increase. One of the primary reasons is the reliance on fossil fuels for energy production within factories. Many manufacturing processes require substantial energy input, often derived from coal, oil, and natural gas, which leads to high levels of CO2 emissions. Additionally, as countries industrialize and seek to boost economic growth, the demand for energy-intensive manufacturing processes escalates, further exacerbating emissions.
Another contributing factor is the inefficiency of outdated machinery and manufacturing practices. Many facilities operate with legacy systems that have not been upgraded for energy efficiency, resulting in excessive energy consumption. The lack of investment in clean technologies and sustainable practices also plays a role, as manufacturers often prioritize short-term profitability over long-term environmental impacts. Furthermore, increased complexity in supply chains can lead to higher emissions, as transportation and logistics related to product distribution add to the overall carbon footprint. Addressing these issues requires a commitment to innovation, investment in cleaner technologies, and a shift towards more sustainable manufacturing practices.
| Sector | Carbon Emissions (MTCO2E) | Growth Rate (%) | Contributing Factors | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemicals | 1,200 | 3.1 | Increased production, outdated technology | Adoption of green chemistry, energy-efficient processes |
| Metals | 900 | 4.5 | Coal dependency, energy-intensive processes | Switch to renewable energy sources, recycling |
| Textiles | 650 | 2.8 | High water and energy consumption | Sustainable materials, water-efficient techniques |
| Cement | 1,700 | 5.0 | Process emissions, large production scale | Alternative binders, carbon capture technology |
| Food Processing | 480 | 3.0 | Transportation, refrigeration | Local sourcing, energy-efficient equipment |
In recent years, the rise in manufacturing carbon emissions has become a pivotal factor contributing to global climate change. The manufacturing sector is responsible for a significant share of greenhouse gases, primarily due to the reliance on fossil fuels for energy and the production processes that emit carbon dioxide and other pollutants. These emissions trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to a rise in global temperatures and causing severe weather patterns, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems.
The impact of increased carbon emissions extends beyond environmental degradation; it poses risks to public health and economic stability. Elevated levels of carbon pollution can worsen air quality, leading to respiratory diseases and other health issues among populations. Moreover, climate change driven by escalating emissions threatens food security through erratic weather conditions that affect agricultural productivity. Additionally, the economic burden of natural disasters exacerbated by climate change can strain resources and undermine development efforts, making it imperative to address the sources of manufacturing emissions swiftly and effectively. This challenge calls for a concerted effort towards cleaner manufacturing technologies and sustainable practices that can mitigate the adverse effects on our planet.
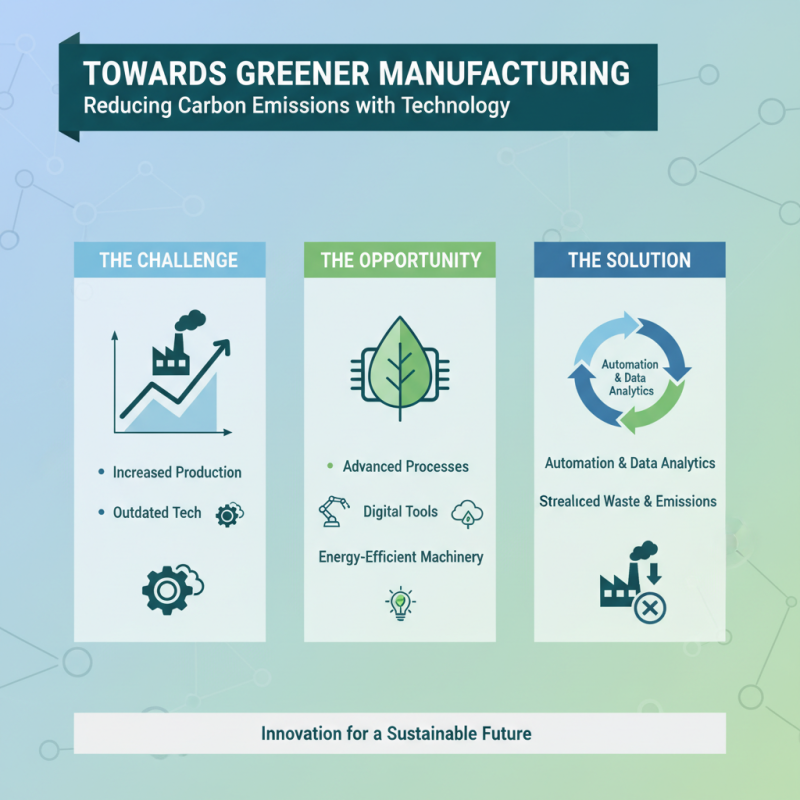
The rise of manufacturing carbon emissions is a pressing issue that can be attributed to various factors, including increased production demands and outdated technologies. However, technological advances present both challenges and opportunities for reducing these emissions. Innovations such as advanced manufacturing processes, digital tools, and energy-efficient machinery can play a crucial role in minimizing the environmental impact. For example, implementing automation and data analytics can streamline operations, leading to enhanced efficiency and reduced waste, thereby lowering the overall carbon footprint.
Tips for manufacturers looking to upgrade their technologies to combat emissions include investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, which can significantly decrease reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, companies should explore options for recycling and reusing materials in their production processes. Embracing circular economy principles can not only reduce emissions but also create a sustainable business model that appeals to environmentally conscious consumers.
While adopting new technologies can require substantial initial investment, the long-term benefits are considerable. Manufacturers should focus on continuous improvement and the integration of sustainability into their core operations. This approach not only addresses regulatory pressures but also positions companies as leaders in the transition towards a low-carbon economy, ensuring resilience in an evolving market landscape.
As manufacturing carbon emissions continue to rise, the role of governmental policy interventions becomes increasingly critical. In 2021, a report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) indicated that the manufacturing sector accounted for approximately 22% of global CO2 emissions. With rising energy demands and production levels, this figure is expected to grow unless robust policy measures are implemented. Governments can play a pivotal role by establishing stricter emissions regulations, providing tax incentives for green technologies, and supporting research initiatives focused on sustainability in manufacturing processes.
Implementing policies that encourage the adoption of renewable energy sources is essential. For instance, a transition to renewable energy in manufacturing could potentially reduce carbon emissions by up to 70%, according to a 2022 study by the World Resources Institute. Additionally, investing in infrastructure that promotes energy efficiency can help manufacturers cut down on waste and emissions.
Tips for manufacturers looking to align with these policies include evaluating their energy consumption and exploring energy-efficient technologies. Regular audits and assessments of manufacturing processes can identify areas for improvement, while collaboration with governmental programs can provide financial support for adopting cleaner technologies. Engaging in public-private partnerships may also facilitate access to innovative strategies and resources aimed at reducing carbon footprints effectively.
Sustainable practices in manufacturing are increasingly crucial for combating rising carbon emissions, which have surged by over 60% since 1990 due to industrial activities, as reported by the World Bank. Transitioning to greener manufacturing processes can significantly mitigate these emissions, with studies indicating that adopting energy-efficient technologies could reduce the carbon footprint of manufacturing by up to 30%. Techniques such as using renewable energy sources, optimizing supply chains, and implementing circular economy principles can play a pivotal role in this transformation.
One promising strategy is the integration of smart manufacturing technologies. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, smart manufacturing can enhance energy efficiency by 10-20% through better process control and real-time data analysis. Additionally, manufacturers can invest in sustainable materials and waste reduction practices. The Ellen MacArthur Foundation states that shifting to a circular economy for plastics alone could save the industry up to $200 billion per year while dramatically lowering greenhouse gas emissions. By prioritizing these sustainable practices, the manufacturing sector can not only comply with regulatory pressures but also position itself as a leader in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
This chart illustrates carbon emissions produced by various manufacturing sectors in million metric tons for the year 2023. Notably, the Chemicals sector has the highest emissions, highlighting the need for sustainable practices and strategies to mitigate environmental impact.





